본 게시물은 CloudNet@에서 진행하는 AEWS (Amazon EKS Workshop Study) 스터디에 참여하며 정리한 내용입니다.
0. EKS Autoscaling 개요 및 실습 환경
이번 실습에서 다루고자 하는 "EKS Autoscaling"에 대해 먼저 알아보자. 쿠버네티스 장점 중 하나인 쿠버네티스 파드 오토스케일링 (링크)은 파드 자체 관점으로 살펴보면 크게 "수평적인 (Horizontal)" 및 "수직적인 (Vertical)" 파드 오토스케일링(Pod Autoscaling)을 위한 2가지로 나누어볼 수 있으며 이를 각각 HPA, VPA라고 부른다. 아래 그림에서와 같이 HPA는 동등한 CPU/메모리 할당이 이루어진 파드 개수를 늘리는 방향으로 이루어지며 VPA는 파드에 할당된 CPU/메모리와 같은 할당량을 늘리는 방식으로 이루어진다.

또한 쿠버네티스 클러스터 전체 관점에서 보면 클러스터 자체를 오토스케일링하는 Cluster Austoscaler (CA/ CAS) 전략도 있다. 이는 워커 노드 사용량이 한계에 도달하여 신규 파드 배포를 수용하지 못할 때 발생하는 상황으로 클러스터 내 워커 노드를 늘리는 방향으로 스케일링이 이루어지는 전략이다.
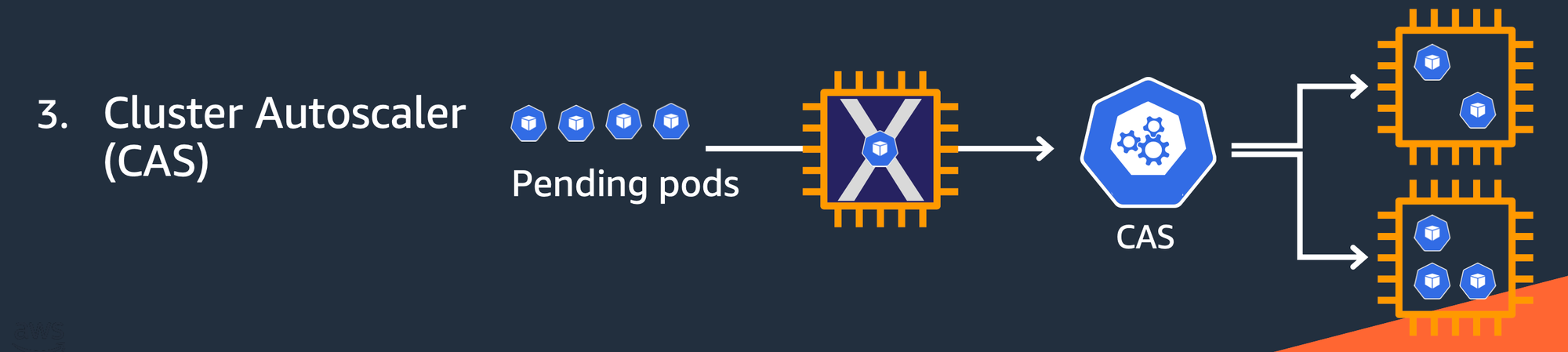
EKS에서는 Karpenter를 사용하여 클러스터 오토스케일링 전략을 적용할 수 있다. Karpenter가 클러스터에 설치되면 Karpenter는 예약되지 않은 파드의 전체 리소스 요청을 관찰하고 새 노드를 시작하고 종료하는 결정을 내림으로써 예약 대기 시간과 인프라 비용을 줄인다. 이를 위해 Karpenter는 Kubernetes 클러스터 내의 이벤트를 관찰한 다음 Amazon EC2와 같은 컴퓨팅 서비스에 전송을 하는 방식으로 동작한다 (Amazon EC2 뿐만 아니라 다른 클라우드 환경도 지원하는 오픈 소스라고 한다).

이번 실습 역시 지난 실습 (링크)에서 전제된 2가지(Route 53: 외부 도메인에 대한 Zone 설정, Certificate Manager (ACM): 해당 도메인에 대한 하위 도메인 모두를 허용하는 * 인증서)가 준비되어야 실습이 가능하다.
다음과 같이 명령어로 실행하여 배포를 진행하였다.
# YAML 파일 다운로드
curl -O https://s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/cloudformation.cloudneta.net/K8S/eks-oneclick4.yaml
# CloudFormation 스택 배포
aws cloudformation deploy --template-file eks-oneclick4.yaml --stack-name myeks --parameter-overrides KeyName=kp-ian SgIngressSshCidr=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)/32 MyIamUserAccessKeyID=`cat ~/.aws/credentials | grep aws_access_key_id | awk '{print $3}'` MyIamUserSecretAccessKey=`cat ~/.aws/credentials | grep aws_secret_access_key | awk '{print $3}'` ClusterBaseName=myeks --region ap-northeast-2
# CloudFormation 스택 배포 완료 후 작업용 EC2 IP 출력
aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text
# 작업용 EC2 SSH 접속
ssh -i ~/.ssh/kp-ian.pem ec2-user@$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text)
or
ssh -i ~/.ssh/kp-ian.pem root@$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text)
~ password: qwe123
이후 지난 번 실습과 동일하게 3개 워커 노드에 대한 IP 주소를 가져와 환경 변수에 저장하고, kube-ops-view 설치, AWS LB Controller 설치, gp3 스토리지 클래스 생성, 노드 보안그룹 ID 확인까지 동일하게 수행한다.
이후, 지난 번 실습 4번에 언급된 프로메테우스 & 그라파나 설치를 아래 내용을 참고하여 진행해보자. 이번 실습은 EKS Autoscaler인 만큼 프로메테우스를 yaml로 설치할 때 다음 옵션을 활성화하도록 한다. 그라파나는 추천 대시보드: 15757, 17900, 15172를 Import해두도록 하자.
# monitor-values.yaml - "prometheus:" 하위 요소로 "prometheusSpec:" 및 "ingress:"와 동등하게 추가
verticalPodAutoscaler:
enabled: true

그리고 EKS Node Viewer를 설치한다. EKS 클러스터 내 동적 노드 사용량(usage)를 시각화해주는 명령 도구로, Karpenter와의 통합을 시연하기 위해 AWS에서 내부 도구 시작된 도구라고 한다. 다음과 같이 예약된 파드 리소스 요청, 할당 가능한 노드 용량을 표시해준다.
# go 설치
wget https://go.dev/dl/go1.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
go version
go version go1.22.1 linux/amd64
# EKS Node Viewer 설치 : 약 2분 이상 소요
go install github.com/awslabs/eks-node-viewer/cmd/eks-node-viewer@latest
# [신규 터미널] EKS Node Viewer 접속
cd ~/go/bin && ./eks-node-viewer
혹은
cd ~/go/bin && ./eks-node-viewer --resources cpu,memory
명령 샘플
# Standard usage
./eks-node-viewer
# Display both CPU and Memory Usage
./eks-node-viewer --resources cpu,memory
# Karenter nodes only
./eks-node-viewer --node-selector "karpenter.sh/provisioner-name"

1. HPA - Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
kube-ops-view와 그라파나에서 모니터링을 같이 해보고자 한다. 그라파나의 경우 17125 대시보드를 기반으로 모니터링을 할 예정인데 다음과 같은 diff 사항을 반영하여 17125 대시보드를 수정한 json 파일을 적용하도록 하자.
104c104
< "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_status_desired_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", namespace=\"$namespace\", horizontalpodautoscaler=\"$horizontalpodautoscaler\"}",
---
> "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_status_desired_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
185c185
< "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_status_current_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", namespace=\"$namespace\", horizontalpodautoscaler=\"$horizontalpodautoscaler\"}",
---
> "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_status_current_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
266c266
< "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_spec_min_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", namespace=\"$namespace\", horizontalpodautoscaler=\"$horizontalpodautoscaler\"}",
---
> "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_spec_min_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
347c347
< "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_spec_max_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", horizontalpodautoscaler=\"$horizontalpodautoscaler\", namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
---
> "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_spec_max_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\"}",
417c417
< "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_status_desired_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", horizontalpodautoscaler=\"$horizontalpodautoscaler\",namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
---
> "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_status_desired_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\",namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
424c424
< "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_status_current_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", horizontalpodautoscaler=\"$horizontalpodautoscaler\",namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
---
> "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_status_current_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\",namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
431c431
< "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_spec_max_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", horizontalpodautoscaler=\"$horizontalpodautoscaler\",namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
---
> "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_spec_max_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\",namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
439c439
< "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_spec_min_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\", horizontalpodautoscaler=\"$horizontalpodautoscaler\",namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
---
> "expr": "kube_horizontalpodautoscaler_spec_min_replicas{job=\"kube-state-metrics\",namespace=\"$namespace\"}",
592c592
< }
\ No newline at end of file
---
> }

그 다음, CPU와 메모리 리밋이 명시되어 있는 php-apache.yaml 에 따라 파드를 실행하여 부하를 발생시켜보고자 한다. 먼저 다음과 같이 부하를 발생시킬 준비를 해보자.
# Run and expose php-apache server
curl -s -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/website/main/content/en/examples/application/php-apache.yaml
cat php-apache.yaml | yh
kubectl apply -f php-apache.yaml
# 확인
kubectl exec -it deploy/php-apache -- cat /var/www/html/index.php
...
# 모니터링 : 터미널2개 사용
watch -d 'kubectl get hpa,pod;echo;kubectl top pod;echo;kubectl top node'
kubectl exec -it deploy/php-apache -- top
# 접속
PODIP=$(kubectl get pod -l run=php-apache -o jsonpath={.items[0].status.podIP})
curl -s $PODIP; echo

준비가 완료되었으니 HPA 생성 및 부하 발생 후 오토스케일링을 테스트해보자.
# Create the HorizontalPodAutoscaler : requests.cpu=200m - 알고리즘
# Since each pod requests 200 milli-cores by kubectl run, this means an average CPU usage of 100 milli-cores.
kubectl autoscale deployment php-apache --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
kubectl describe hpa
...
Metrics: ( current / target )
resource cpu on pods (as a percentage of request): 0% (1m) / 50%
Min replicas: 1
Max replicas: 10
Deployment pods: 1 current / 1 desired
...
# HPA 설정 확인
kubectl get hpa php-apache -o yaml | kubectl neat | yh
spec:
minReplicas: 1 # [4] 또는 최소 1개까지 줄어들 수도 있습니다
maxReplicas: 10 # [3] 포드를 최대 5개까지 늘립니다
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache # [1] php-apache 의 자원 사용량에서
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50 # [2] CPU 활용률이 50% 이상인 경우
# 반복 접속 1 (파드1 IP로 접속) >> 증가 확인 후 중지
while true;do curl -s $PODIP; sleep 0.5; done
# 반복 접속 2 (서비스명 도메인으로 파드들 분산 접속) >> 증가 확인(몇개까지 증가되는가? 그 이유는?) 후 중지 >> 중지 5분 후 파드 갯수 감소 확인
# Run this in a separate terminal
# so that the load generation continues and you can carry on with the rest of the steps
kubectl run -i --tty load-generator --rm --image=busybox:1.28 --restart=Never -- /bin/sh -c "while sleep 0.01; do wget -q -O- http://php-apache; done"
부하를 발생시키면서 점차 오토스케일링이 이루어지는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
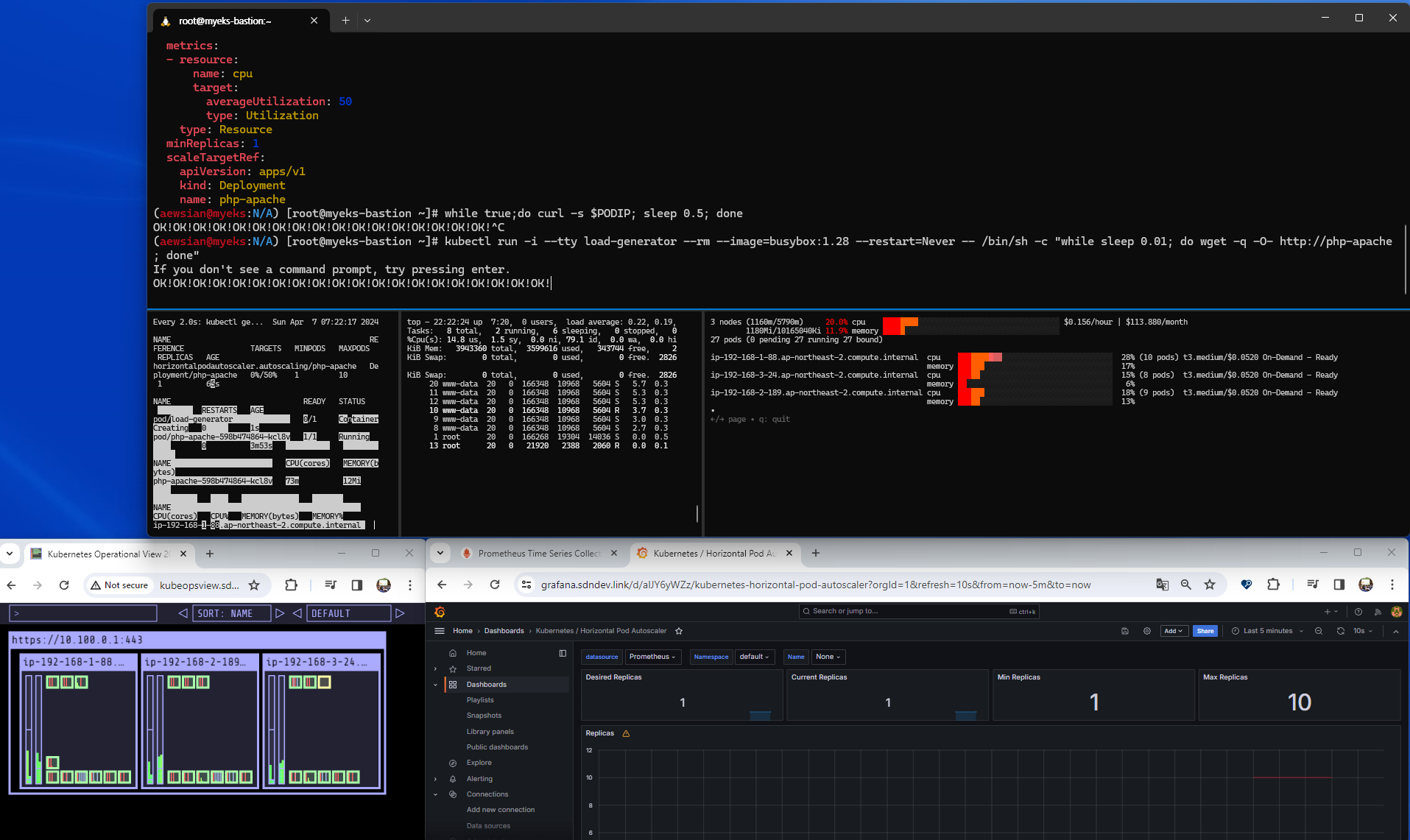
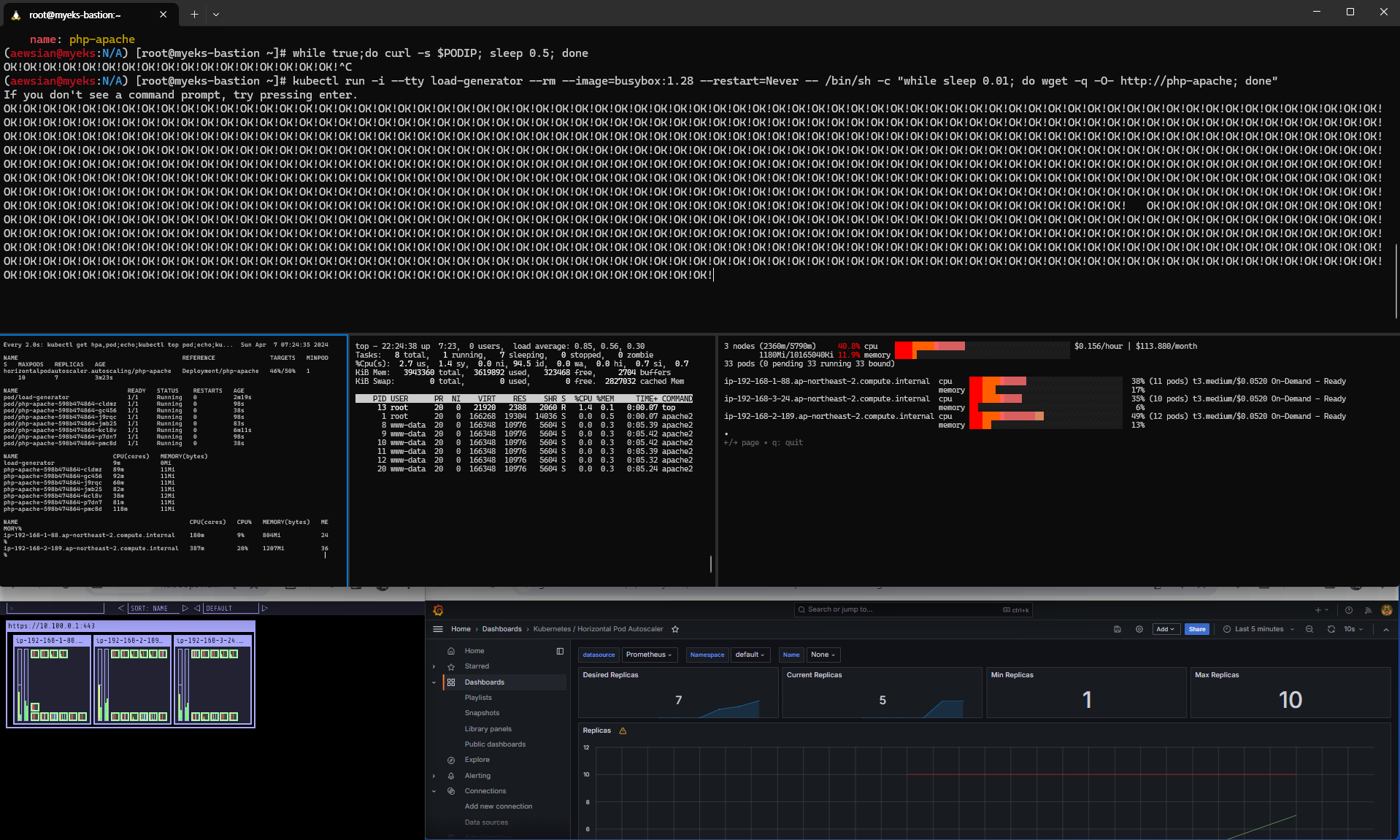
로드가 계속 발생하면서 처음에는 CPU 활용율이 증가하여 파드 확장이 이루어지다가, 파드 개수가 어느 정도 늘어난 다음에는 CPU 사용률이 안정적으로 되어 시간이 계속 지나도 더 이상 파드 확장이 이루어지지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이렇게 확인한 다음에는 Ctrl+C를 눌러 반복 부하를 중지하고 조금 기다려보자. 오토스케일링이 이루어져 파드가 1개로 변경된 결과를 확인할 수 있다.

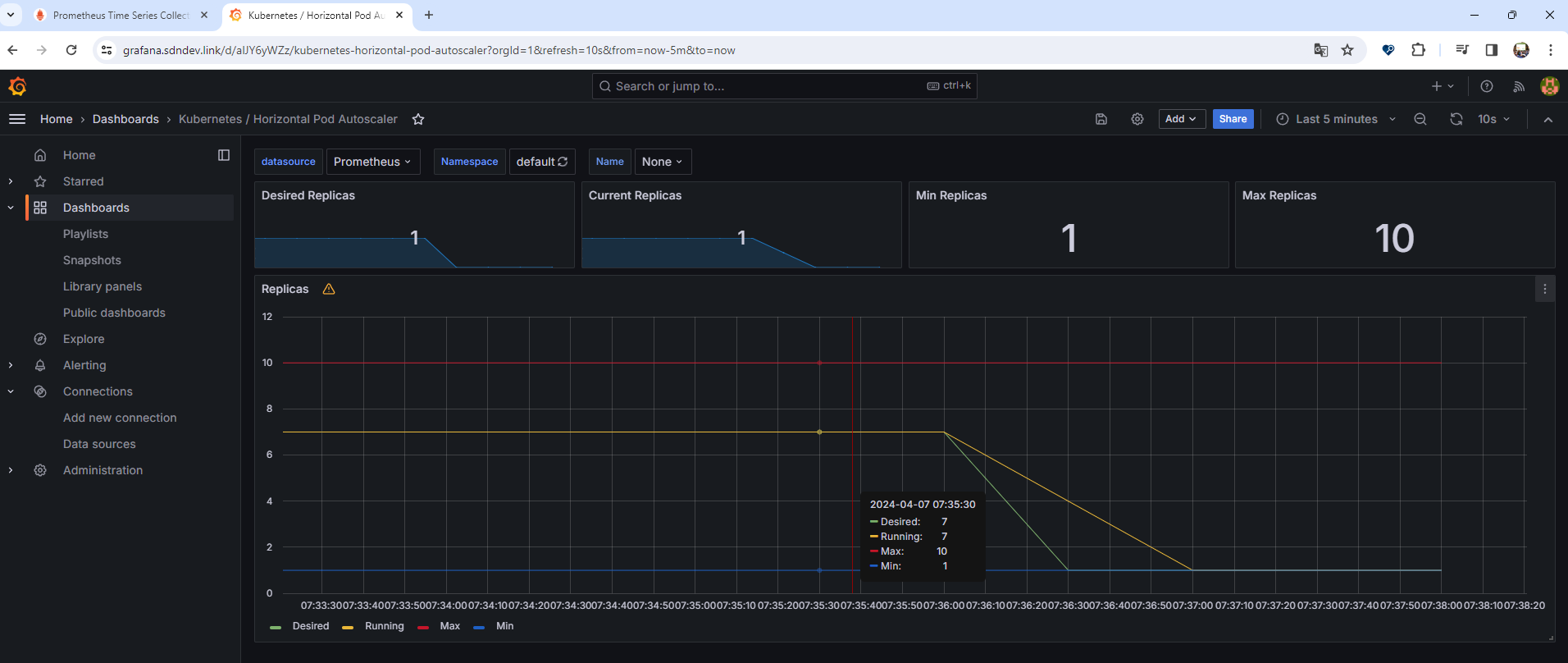
확인 후 다음 명령어 실행을 통해 오브젝트를 삭제하자.
kubectl delete deploy,svc,hpa,pod --all2. KEDA - Kubernetes based Event Driven Autoscaler
KEDA는 기존에 CPU와 메모리와 같은 메트릭을 기반으로 스케일링 여부를 결정하는 방식과 달리 특정 이벤트를 기반으로 스케일링 여부를 결정할 수 있도록 지원한다.
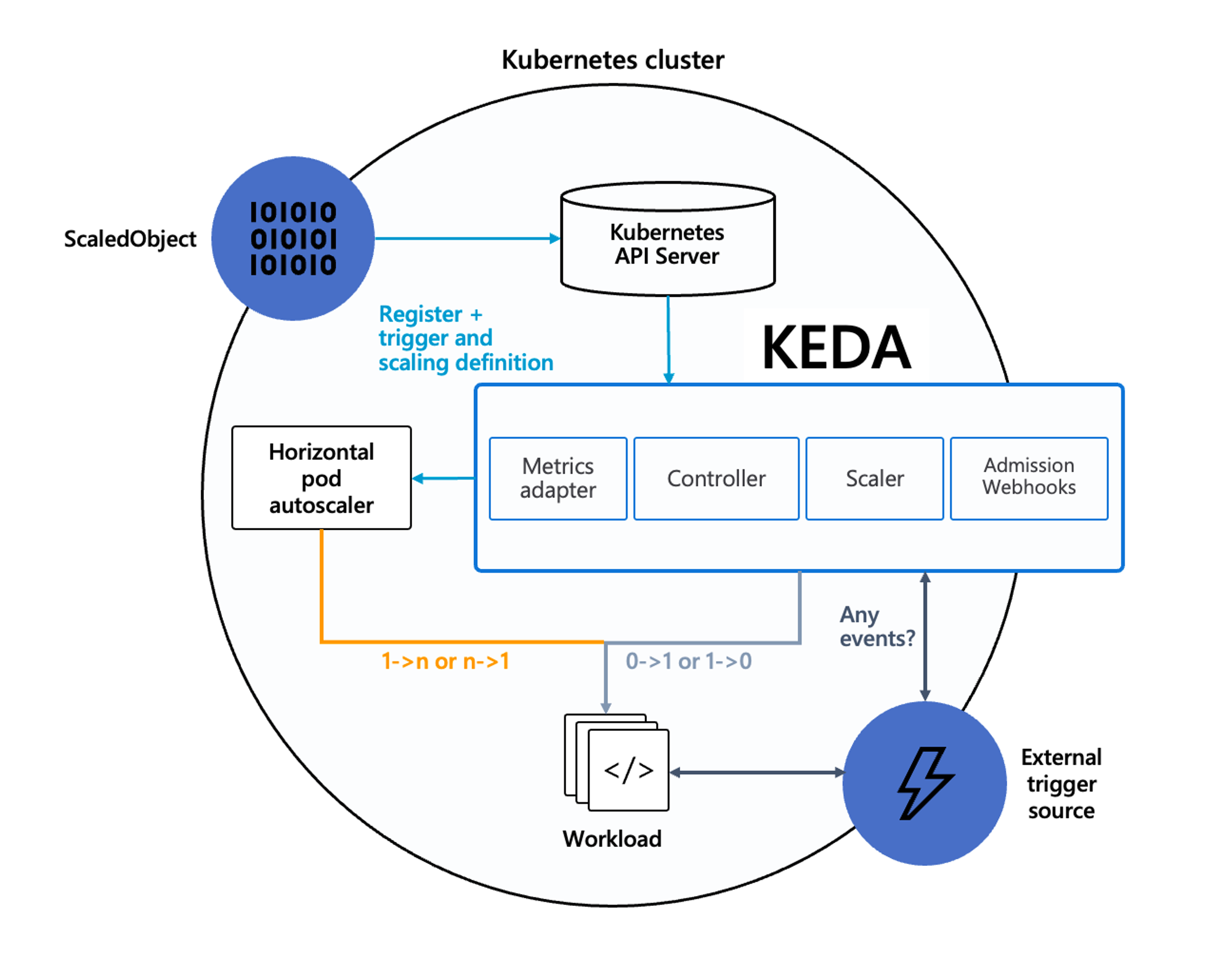
KEDA 대시보드를 그라파나에 Import한 다음 아래를 실행하여 결과를 확인해보도록 하자.
# KEDA 설치
cat <<EOT > keda-values.yaml
metricsServer:
useHostNetwork: true
prometheus:
metricServer:
enabled: true
port: 9022
portName: metrics
path: /metrics
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
podMonitor:
# Enables PodMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
operator:
enabled: true
port: 8080
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
podMonitor:
# Enables PodMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
webhooks:
enabled: true
port: 8080
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus webhooks
enabled: true
EOT
kubectl create namespace keda
helm repo add kedacore https://kedacore.github.io/charts
helm install keda kedacore/keda --version 2.13.0 --namespace keda -f keda-values.yaml
# KEDA 설치 확인
kubectl get all -n keda
kubectl get validatingwebhookconfigurations keda-admission
kubectl get validatingwebhookconfigurations keda-admission -o=json | kubectl neat | yh
kubectl get crd | grep keda
# keda 네임스페이스에 디플로이먼트 생성
kubectl apply -f php-apache.yaml -n keda
kubectl get pod -n keda
# ScaledObject 정책 생성 : cron
cat <<EOT > keda-cron.yaml
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: php-apache-cron-scaled
spec:
minReplicaCount: 0
maxReplicaCount: 2
pollingInterval: 30
cooldownPeriod: 300
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
triggers:
- type: cron
metadata:
timezone: Asia/Seoul
start: 00,15,30,45 * * * *
end: 05,20,35,50 * * * *
desiredReplicas: "1"
EOT
kubectl apply -f keda-cron.yaml -n keda
# 그라파나 대시보드 추가
# 모니터링
watch -d 'kubectl get ScaledObject,hpa,pod -n keda'
kubectl get ScaledObject -w
# 확인
kubectl get ScaledObject,hpa,pod -n keda
kubectl get hpa -o jsonpath={.items[0].spec} -n keda | jq
...
"metrics": [
{
"external": {
"metric": {
"name": "s0-cron-Asia-Seoul-00,15,30,45xxxx-05,20,35,50xxxx",
"selector": {
"matchLabels": {
"scaledobject.keda.sh/name": "php-apache-cron-scaled"
}
}
},
"target": {
"averageValue": "1",
"type": "AverageValue"
}
},
"type": "External"
}
# KEDA 및 deployment 등 삭제
kubectl delete -f keda-cron.yaml -n keda && kubectl delete deploy php-apache -n keda && helm uninstall keda -n keda
kubectl delete namespace keda
아래 대시보드 스크린샷과 같이 20분에 end 이벤트가 cron으로부터 발생하여 파드가 종료되었다가, desiredReplicas 개수가 1로 설정되어 있으므로 다시 1개 파드가 재생성된 것을 확인할 수 있었다.

3. VPA - Vertical Pod Autoscaler
다음 코드를 통해 VPA를 먼저 배포한다.
# 코드 다운로드
git clone https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler.git
cd ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/
tree hack
# openssl 버전 확인
openssl version
OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
# openssl 1.1.1 이상 버전 확인
yum install openssl11 -y
openssl11 version
OpenSSL 1.1.1g FIPS 21 Apr 2020
# 스크립트파일내에 openssl11 수정
sed -i 's/openssl/openssl11/g' ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/pkg/admission-controller/gencerts.sh
# Deploy the Vertical Pod Autoscaler to your cluster with the following command.
watch -d kubectl get pod -n kube-system
cat hack/vpa-up.sh
./hack/vpa-up.sh
kubectl get crd | grep autoscaling
kubectl get mutatingwebhookconfigurations vpa-webhook-config
kubectl get mutatingwebhookconfigurations vpa-webhook-config -o json | jq
그 다음 공식 예제를 통해 VPA를 실습해보자. 파드가 실행되면 약 2-3분 뒤에 pod resource.request가 VPA에 의해 수정이 이루어진다고 한다.
# 모니터링
watch -d "kubectl top pod;echo "----------------------";kubectl describe pod | grep Requests: -A2"
# 공식 예제 배포
cd ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/
cat examples/hamster.yaml | yh
kubectl apply -f examples/hamster.yaml && kubectl get vpa -w
# 파드 리소스 Requestes 확인
kubectl describe pod | grep Requests: -A2
Requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
--
Requests:
cpu: 587m
memory: 262144k
--
Requests:
cpu: 587m
memory: 262144k
# VPA에 의해 기존 파드 삭제되고 신규 파드가 생성됨
kubectl get events --sort-by=".metadata.creationTimestamp" | grep VPA
2m16s Normal EvictedByVPA pod/hamster-5bccbb88c6-s6jkp Pod was evicted by VPA Updater to apply resource recommendation.
76s Normal EvictedByVPA pod/hamster-5bccbb88c6-jc6gq Pod was evicted by VPA Updater to apply resource recommendation.

이 때 CPU와 메모리에 대한 사항은 프로메테우스 다음 메트릭을 통해 직접 모니터링도 가능하며
kube_customresource_vpa_containerrecommendations_target{resource="cpu"}
kube_customresource_vpa_containerrecommendations_target{resource="memory"}
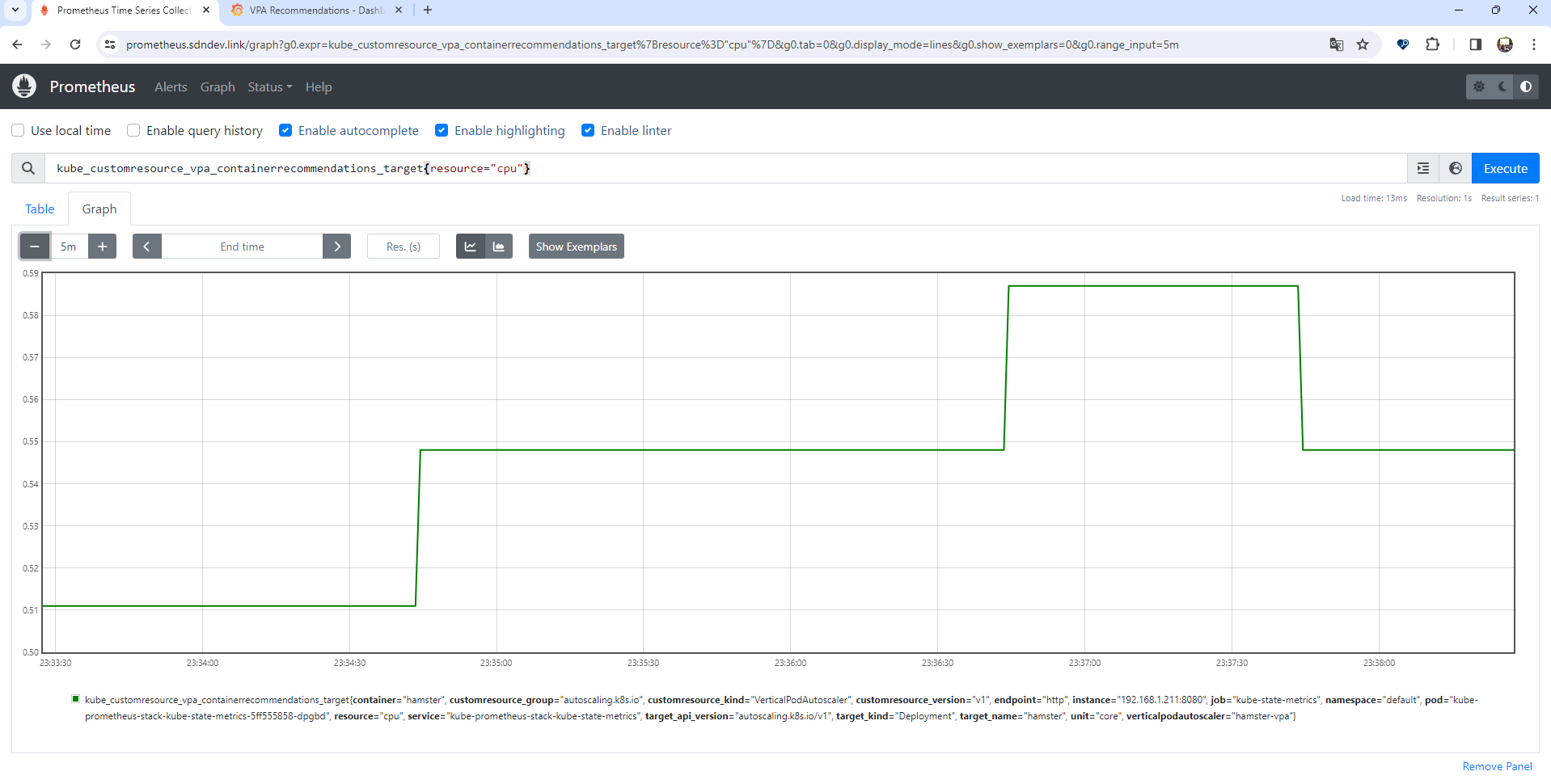
그라파나 대시보드를 통해 시각화된 모니터링 결과를 확인할 수도 있다.

실습을 다 한 이후에는 아래 명령어를 실행하여 리소스를 제거하도록 하자.
kubectl delete -f examples/hamster.yaml && cd ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/ && ./hack/vpa-down.sh
4. CA - Cluster Autoscaler
이제 EKS Workshop에 설명되어 있는 Cluster Scaling 부분을 실습해보도록 하자. 다음과 같은 환경에 해당한다.
- Cluster Autoscale 동작을 하기 위한 cluster-autoscaler 파드(디플로이먼트)를 배치
- Cluster Autoscaler(CA)는 pending 상태인 파드가 존재할 경우, 워커 노드를 스케일 아웃
- 특정 시간을 간격으로 사용률을 확인하여 스케일 인/아웃을 수행 & AWS에서는 Auto Scaling Group(ASG)을 사용하여 Cluster Autoscaler를 적용

실습 전 EKS 노드에 아래 tag가 들어가 있는지 확인해보도록 하자.
# k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled : true
# k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/myeks : owned
aws ec2 describe-instances --filters Name=tag:Name,Values=$CLUSTER_NAME-ng1-Node --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].Tags[*]" --output yaml | yh
# 현재 autoscaling(ASG) 정보 확인
# aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='클러스터이름']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups \
--query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" \
--output table
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| eks-ng1-44c41109-daa3-134c-df0e-0f28c823cb47 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
# MaxSize 6개로 수정
export ASG_NAME=$(aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].AutoScalingGroupName" --output text)
aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 3 --desired-capacity 3 --max-size 6
# 확인
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| eks-ng1-c2c41e26-6213-a429-9a58-02374389d5c3 | 3 | 6 | 3 |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
# 배포 : Deploy the Cluster Autoscaler (CA)
curl -s -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/aws/examples/cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
sed -i "s/<YOUR CLUSTER NAME>/$CLUSTER_NAME/g" cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
kubectl apply -f cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get pod -n kube-system | grep cluster-autoscaler
kubectl describe deployments.apps -n kube-system cluster-autoscaler
kubectl describe deployments.apps -n kube-system cluster-autoscaler | grep node-group-auto-discovery
--node-group-auto-discovery=asg:tag=k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled,k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/myeks
# (옵션) cluster-autoscaler 파드가 동작하는 워커 노드가 퇴출(evict) 되지 않게 설정
kubectl -n kube-system annotate deployment.apps/cluster-autoscaler cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/safe-to-evict="false"
# 모니터링
kubectl get nodes -w
while true; do kubectl get node; echo "------------------------------" ; date ; sleep 1; done
while true; do aws ec2 describe-instances --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PrivateIPAdd:PrivateIpAddress,InstanceName:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" --filters Name=instance-state-name,Values=running --output text ; echo "------------------------------"; date; sleep 1; done
# Deploy a Sample App
# We will deploy an sample nginx application as a ReplicaSet of 1 Pod
cat <<EoF> nginx.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-to-scaleout
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
service: nginx
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx-to-scaleout
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
EoF
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
kubectl get deployment/nginx-to-scaleout
# Scale our ReplicaSet
# Let’s scale out the replicaset to 15
kubectl scale --replicas=15 deployment/nginx-to-scaleout && date
# 확인
kubectl get pods -l app=nginx -o wide --watch
kubectl -n kube-system logs -f deployment/cluster-autoscaler
# 노드 자동 증가 확인
kubectl get nodes
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups \
--query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" \
--output table
./eks-node-viewer --resources cpu,memory
혹은
./eks-node-viewer
# 디플로이먼트 삭제
kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml && date
# 노드 갯수 축소 : 기본은 10분 후 scale down 됨, 물론 아래 flag 로 시간 수정 가능 >> 그러니 디플로이먼트 삭제 후 10분 기다리고 나서 보자!
# By default, cluster autoscaler will wait 10 minutes between scale down operations,
# you can adjust this using the --scale-down-delay-after-add, --scale-down-delay-after-delete,
# and --scale-down-delay-after-failure flag.
# E.g. --scale-down-delay-after-add=5m to decrease the scale down delay to 5 minutes after a node has been added.
# 터미널1
watch -d kubectl get node
실습을 해보면 노드 개수가 부족하여 파드들이 pending이 일어나다가

해당 파드들을 배포하기 위해 오토스케일링이 일어난 것을 확인할 수 있다.

디플로이먼트 삭제 후 10분 정도 지나면 노드 개수가 축소된다.

이후 리소스를 삭제하도록 하자. 만약 노드 개수가 축소되지 않은 상태에서 리소스를 삭제하면 워커 노드가 4개인 상태로 계속 유지가 되는 만큼 수동으로 2개 변경을 하는 명령어를 실행하도록 하자.
# size 수정
aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 3 --desired-capacity 3 --max-size 3
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
# Cluster Autoscaler 삭제
kubectl delete -f cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
5. CPA - Cluster Proportional Autoscaler
CPA는 노드 수 증가에 비례하여 성능 처리가 필요한 애플리케이션 (컨테이너/파드)를 수평으로 자동 확장하는 것을 이야기한다.

helm repo add cluster-proportional-autoscaler https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/cluster-proportional-autoscaler
# CPA규칙을 설정하고 helm차트를 릴리즈 필요
helm upgrade --install cluster-proportional-autoscaler cluster-proportional-autoscaler/cluster-proportional-autoscaler
# nginx 디플로이먼트 배포
cat <<EOT > cpa-nginx.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
resources:
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "64Mi"
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "64Mi"
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOT
kubectl apply -f cpa-nginx.yaml
# CPA 규칙 설정
cat <<EOF > cpa-values.yaml
config:
ladder:
nodesToReplicas:
- [1, 1]
- [2, 2]
- [3, 3]
- [4, 3]
- [5, 5]
options:
namespace: default
target: "deployment/nginx-deployment"
EOF
kubectl describe cm cluster-proportional-autoscaler
# 모니터링
watch -d kubectl get pod
# helm 업그레이드
helm upgrade --install cluster-proportional-autoscaler -f cpa-values.yaml cluster-proportional-autoscaler/cluster-proportional-autoscaler
# 노드 5개로 증가
export ASG_NAME=$(aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].AutoScalingGroupName" --output text)
aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 5 --desired-capacity 5 --max-size 5
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
# 노드 4개로 축소
aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 4 --desired-capacity 4 --max-size 4
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
노드가 5개로 증가하였다.
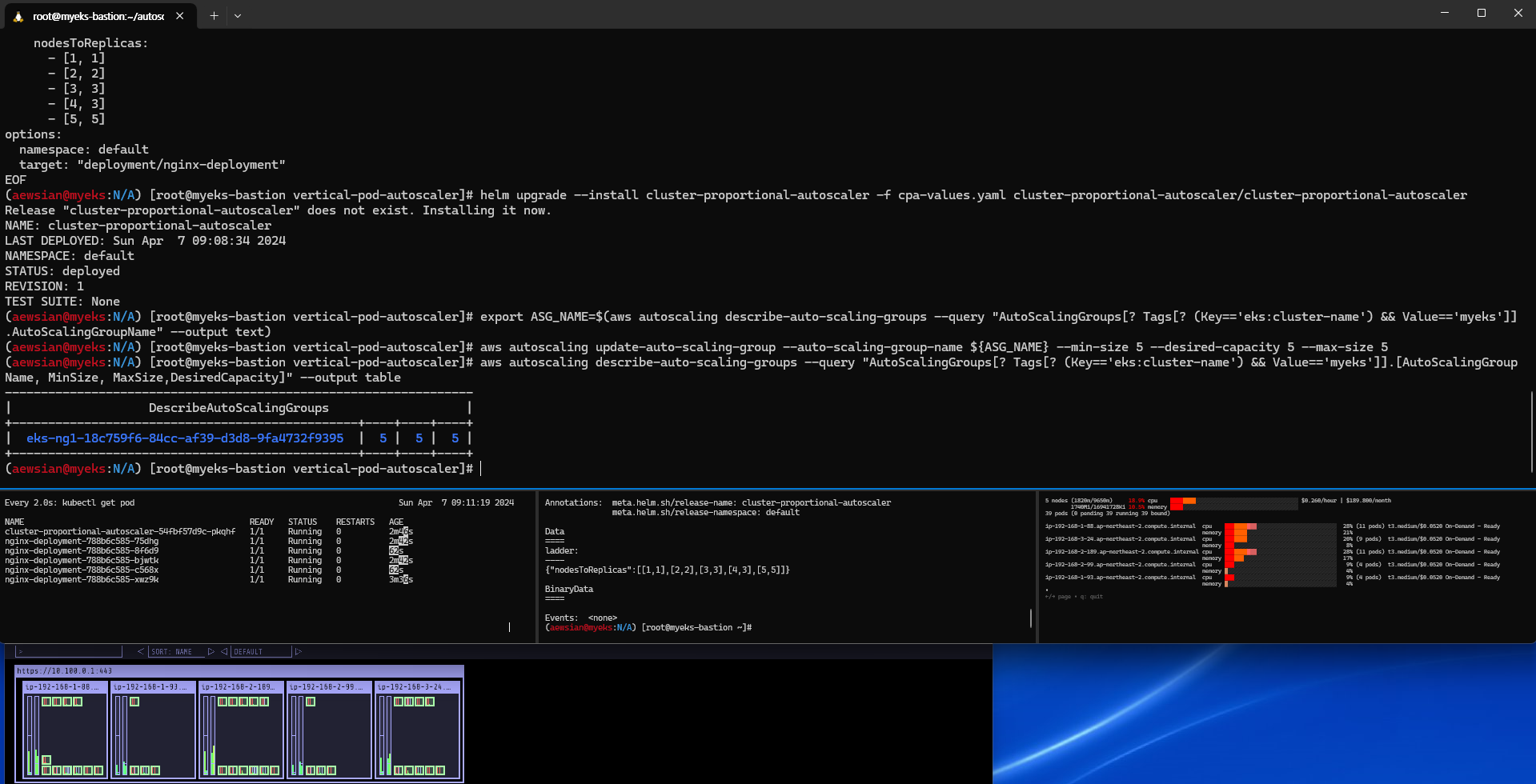
4개로 변경 후 결과 확인


실습을 완료한 다음에는 리소스를 삭제한다.
helm uninstall cluster-proportional-autoscaler && kubectl delete -f cpa-nginx.yaml
여기까지 완료하면 그 다음에는 Karpenter 실습 환경 준비를 위해 현재 EKS 실습 환경을 전부 삭제하자.
eksctl delete cluster --name $CLUSTER_NAME && aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name $CLUSTER_NAME
6. Karpenter: K8s Native Autoscaler
Karpenter는 오픈 소스 노드 수명 주기 관리 솔루션으로 Amazon EC2에서 제공하는 API 레벨과 직접 통신을 하여 수 초만에 컴퓨팅 리소스를 제공하는 이점을 제공한다.

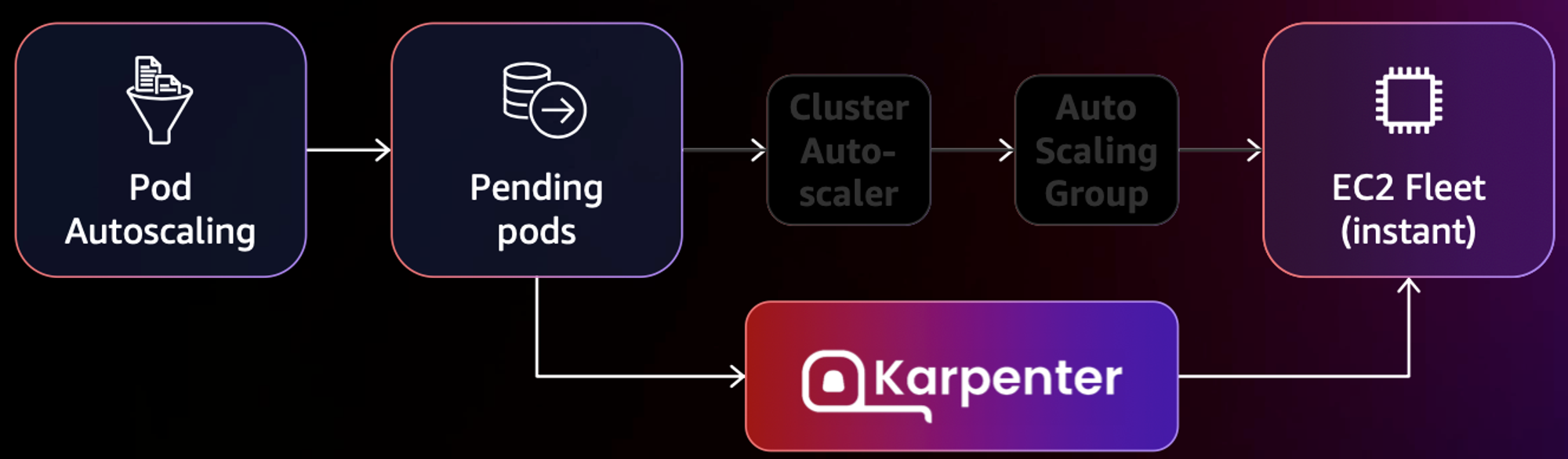
Karpenter 버전이 0.2x 에서 0.3x로 2023년 10월 경 변경되었는데 (링크), 여러 문법 변화가 있는 부분이 있기에 참고하도록 하자.
실습을 위해 기존 EKS 클러스터인 myeks가 완전히 삭제된 이후에 아래 스크립트를 참고하여 실행하도록 하자. myeks2라는 새로운 배포 환경을 사전에 준비한 다음, Karpenter 배포를 위한 환경 준비 및 클러스터 생성, kube-ops-view, Karpenter 설치까지를 진행한다.
# YAML 파일 다운로드
curl -O https://s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/cloudformation.cloudneta.net/K8S/karpenter-preconfig.yaml
# CloudFormation 스택 배포
aws cloudformation deploy --template-file karpenter-preconfig.yaml --stack-name myeks2 --parameter-overrides KeyName=kp-ian SgIngressSshCidr=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)/32 MyIamUserAccessKeyID=`cat ~/.aws/credentials | grep aws_access_key_id | awk '{print $3}'` MyIamUserSecretAccessKey=`cat ~/.aws/credentials | grep aws_secret_access_key | awk '{print $3}'` ClusterBaseName=myeks --region ap-northeast-2
# CloudFormation 스택 배포 완료 후 작업용 EC2 IP 출력
aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks2 --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text
# 작업용 EC2 SSH 접속
ssh -i ~/.ssh/kp-ian.pem ec2-user@$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks2 --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text)
# IP 주소 확인 : 172.30.0.0/16 VPC 대역에서 172.30.1.0/24 대역을 사용 중
ip -br -c addr
# EKS Node Viewer 설치 : 현재 ec2 spec에서는 설치에 다소 시간이 소요됨 = 2분 이상
wget https://go.dev/dl/go1.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
go install github.com/awslabs/eks-node-viewer/cmd/eks-node-viewer@latest
# [터미널1] bin 확인
cd ~/go/bin && ./eks-node-viewer -h
# EKS 배포 완료 후 실행 하자
cd ~/go/bin && ./eks-node-viewer --resources cpu,memory
# 변수 정보 확인
export | egrep 'ACCOUNT|AWS_' | egrep -v 'SECRET|KEY'
# 변수 설정
export KARPENTER_NAMESPACE="kube-system"
export K8S_VERSION="1.29"
export KARPENTER_VERSION="0.35.2"
export TEMPOUT=$(mktemp)
export ARM_AMI_ID="$(aws ssm get-parameter --name /aws/service/eks/optimized-ami/${K8S_VERSION}/amazon-linux-2-arm64/recommended/image_id --query Parameter.Value --output text)"
export AMD_AMI_ID="$(aws ssm get-parameter --name /aws/service/eks/optimized-ami/${K8S_VERSION}/amazon-linux-2/recommended/image_id --query Parameter.Value --output text)"
export GPU_AMI_ID="$(aws ssm get-parameter --name /aws/service/eks/optimized-ami/${K8S_VERSION}/amazon-linux-2-gpu/recommended/image_id --query Parameter.Value --output text)"
export AWS_PARTITION="aws"
export CLUSTER_NAME="${USER}-karpenter-demo"
echo "export CLUSTER_NAME=$CLUSTER_NAME" >> /etc/profile
echo $KARPENTER_VERSION $CLUSTER_NAME $AWS_DEFAULT_REGION $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID $TEMPOUT $ARM_AMI_ID $AMD_AMI_ID $GPU_AMI_ID
# CloudFormation 스택으로 IAM Policy, Role(KarpenterNodeRole-myeks2) 생성 : 3분 정도 소요
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aws/karpenter-provider-aws/v"${KARPENTER_VERSION}"/website/content/en/preview/getting-started/getting-started-with-karpenter/cloudformation.yaml > "${TEMPOUT}" \
&& aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name "Karpenter-${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--template-file "${TEMPOUT}" \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides "ClusterName=${CLUSTER_NAME}"
# 클러스터 생성 : myeks2 EKS 클러스터 생성 19분 정도 소요
eksctl create cluster -f - <<EOF
---
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
version: "${K8S_VERSION}"
tags:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
iam:
withOIDC: true
serviceAccounts:
- metadata:
name: karpenter
namespace: "${KARPENTER_NAMESPACE}"
roleName: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-karpenter
attachPolicyARNs:
- arn:${AWS_PARTITION}:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:policy/KarpenterControllerPolicy-${CLUSTER_NAME}
roleOnly: true
iamIdentityMappings:
- arn: "arn:${AWS_PARTITION}:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/KarpenterNodeRole-${CLUSTER_NAME}"
username: system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}}
groups:
- system:bootstrappers
- system:nodes
managedNodeGroups:
- instanceType: m5.large
amiFamily: AmazonLinux2
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-ng
desiredCapacity: 2
minSize: 1
maxSize: 10
iam:
withAddonPolicies:
externalDNS: true
EOF
# eks 배포 확인
eksctl get cluster
eksctl get nodegroup --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
eksctl get iamidentitymapping --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
eksctl get iamserviceaccount --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
eksctl get addon --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
# default 네임스페이스 적용
kubectl ns default
# 노드 정보 확인
kubectl get node --label-columns=node.kubernetes.io/instance-type,eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType,topology.kubernetes.io/zone
# ExternalDNS
MyDomain=<자신의 도메인>
echo "export MyDomain=<자신의 도메인>" >> /etc/profile
MyDomain=sdndev.link
echo "export MyDomain=sdndev.link" >> /etc/profile
MyDnzHostedZoneId=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones-by-name --dns-name "${MyDomain}." --query "HostedZones[0].Id" --output text)
echo $MyDomain, $MyDnzHostedZoneId
curl -s -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gasida/PKOS/main/aews/externaldns.yaml
MyDomain=$MyDomain MyDnzHostedZoneId=$MyDnzHostedZoneId envsubst < externaldns.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
# kube-ops-view
helm repo add geek-cookbook https://geek-cookbook.github.io/charts/
helm install kube-ops-view geek-cookbook/kube-ops-view --version 1.2.2 --set env.TZ="Asia/Seoul" --namespace kube-system
kubectl patch svc -n kube-system kube-ops-view -p '{"spec":{"type":"LoadBalancer"}}'
kubectl annotate service kube-ops-view -n kube-system "external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname=kubeopsview.$MyDomain"
echo -e "Kube Ops View URL = http://kubeopsview.$MyDomain:8080/#scale=1.5"
# [터미널1] eks-node-viewer
cd ~/go/bin && ./eks-node-viewer --resources cpu,memory
# k8s 확인
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl get node --label-columns=node.kubernetes.io/instance-type,eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType,topology.kubernetes.io/zone
kubectl get pod -n kube-system -owide
kubectl describe cm -n kube-system aws-auth
# Karpenter 설치를 위한 변수 설정 및 확인
export CLUSTER_ENDPOINT="$(aws eks describe-cluster --name "${CLUSTER_NAME}" --query "cluster.endpoint" --output text)"
export KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN="arn:${AWS_PARTITION}:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/${CLUSTER_NAME}-karpenter"
echo "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT} ${KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN}"
# EC2 Spot Fleet의 service-linked-role 생성 확인 : 만들어있는것을 확인하는 거라 아래 에러 출력이 정상!
# If the role has already been successfully created, you will see:
# An error occurred (InvalidInput) when calling the CreateServiceLinkedRole operation: Service role name AWSServiceRoleForEC2Spot has been taken in this account, please try a different suffix.
aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name spot.amazonaws.com || true
# docker logout : Logout of docker to perform an unauthenticated pull against the public ECR
docker logout public.ecr.aws
# helm registry logout
helm registry logout public.ecr.aws
# karpenter 설치
helm install karpenter oci://public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter --version "${KARPENTER_VERSION}" --namespace "${KARPENTER_NAMESPACE}" --create-namespace \
--set "serviceAccount.annotations.eks\.amazonaws\.com/role-arn=${KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN}" \
--set "settings.clusterName=${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--set "settings.interruptionQueue=${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--set controller.resources.requests.cpu=1 \
--set controller.resources.requests.memory=1Gi \
--set controller.resources.limits.cpu=1 \
--set controller.resources.limits.memory=1Gi \
--wait
# 확인
kubectl get-all -n $KARPENTER_NAMESPACE
kubectl get all -n $KARPENTER_NAMESPACE
kubectl get crd | grep karpenter
그 다음 NodePool (참고: 링크)을 설치하도록 하자.
cat <<EOF | envsubst | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1beta1
kind: NodePool
metadata:
name: default
spec:
template:
spec:
requirements:
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values: ["amd64"]
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values: ["linux"]
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["spot"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-category
operator: In
values: ["c", "m", "r"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-generation
operator: Gt
values: ["2"]
nodeClassRef:
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1beta1
kind: EC2NodeClass
name: default
limits:
cpu: 1000
disruption:
consolidationPolicy: WhenUnderutilized
expireAfter: 720h # 30 * 24h = 720h
---
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1beta1
kind: EC2NodeClass
metadata:
name: default
spec:
amiFamily: AL2 # Amazon Linux 2
role: "KarpenterNodeRole-${CLUSTER_NAME}" # replace with your cluster name
subnetSelectorTerms:
- tags:
karpenter.sh/discovery: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" # replace with your cluster name
securityGroupSelectorTerms:
- tags:
karpenter.sh/discovery: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" # replace with your cluster name
amiSelectorTerms:
- id: "${ARM_AMI_ID}"
- id: "${AMD_AMI_ID}"
# - id: "${GPU_AMI_ID}" # <- GPU Optimized AMD AMI
# - name: "amazon-eks-node-${K8S_VERSION}-*" # <- automatically upgrade when a new AL2 EKS Optimized AMI is released. This is unsafe for production workloads. Validate AMIs in lower environments before deploying them to production.
EOF
# 확인
kubectl get nodepool,ec2nodeclass
이제 준비가 완료되었으므로 배포에 대해 스케일업을 시켜보도록 하자.
# pause 파드 1개에 CPU 1개 최소 보장 할당
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: inflate
spec:
replicas: 0
selector:
matchLabels:
app: inflate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: inflate
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
containers:
- name: inflate
image: public.ecr.aws/eks-distro/kubernetes/pause:3.7
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
EOF
# Scale up
kubectl get pod
kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas 5
kubectl logs -f -n "${KARPENTER_NAMESPACE}" -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
kubectl logs -f -n "${KARPENTER_NAMESPACE}" -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller | jq '.'
스케일업을 실행하게 되면 pod수가 많아지는 것에 따라
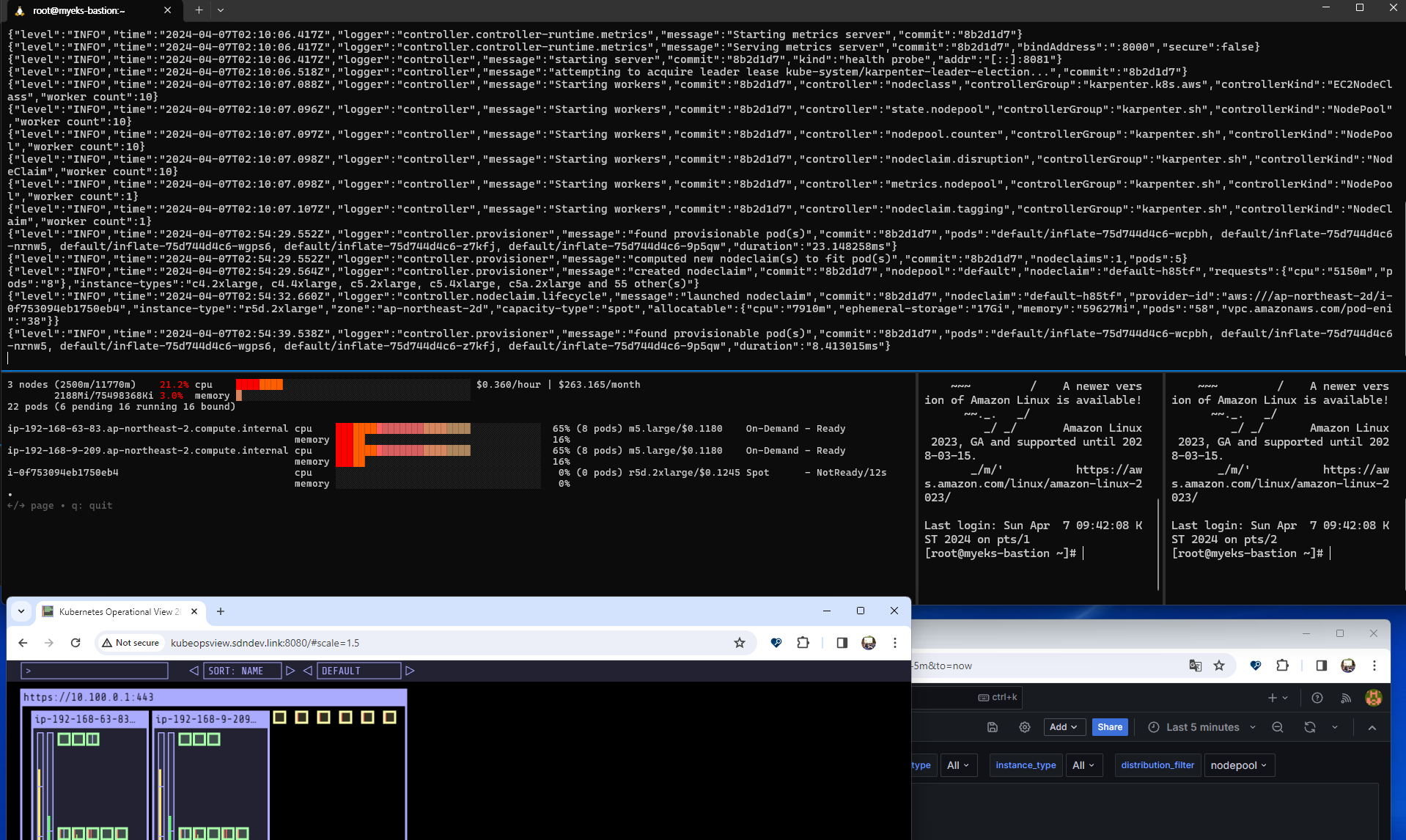
새로운 노드가 생성되어짐을 확인할 수 있다. (확실히 이전 실습에서보다 빠르다)
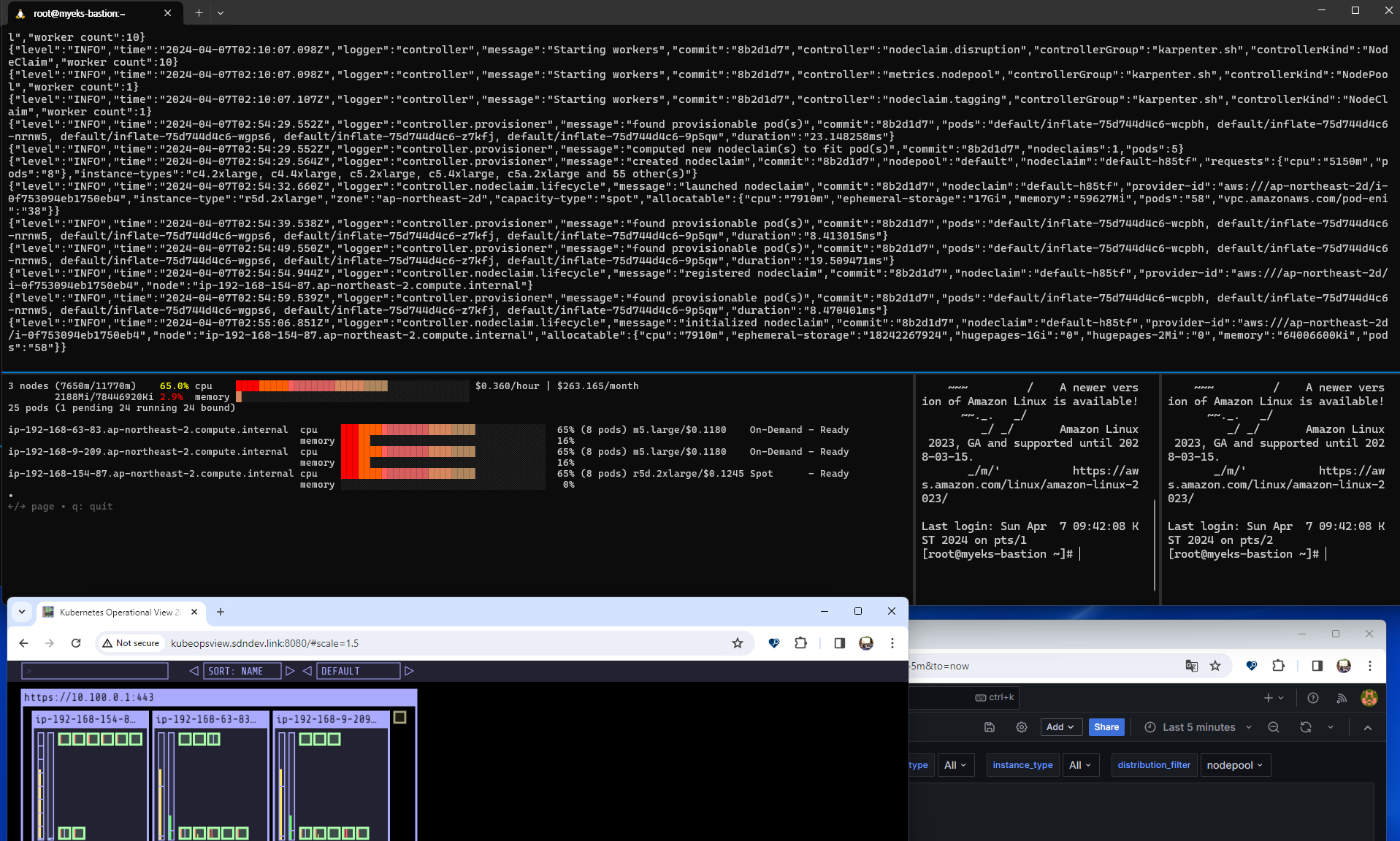
스케일 다운 또한 실습해보자.
kubectl delete deployment inflate && date
kubectl logs -f -n "${KARPENTER_NAMESPACE}" -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
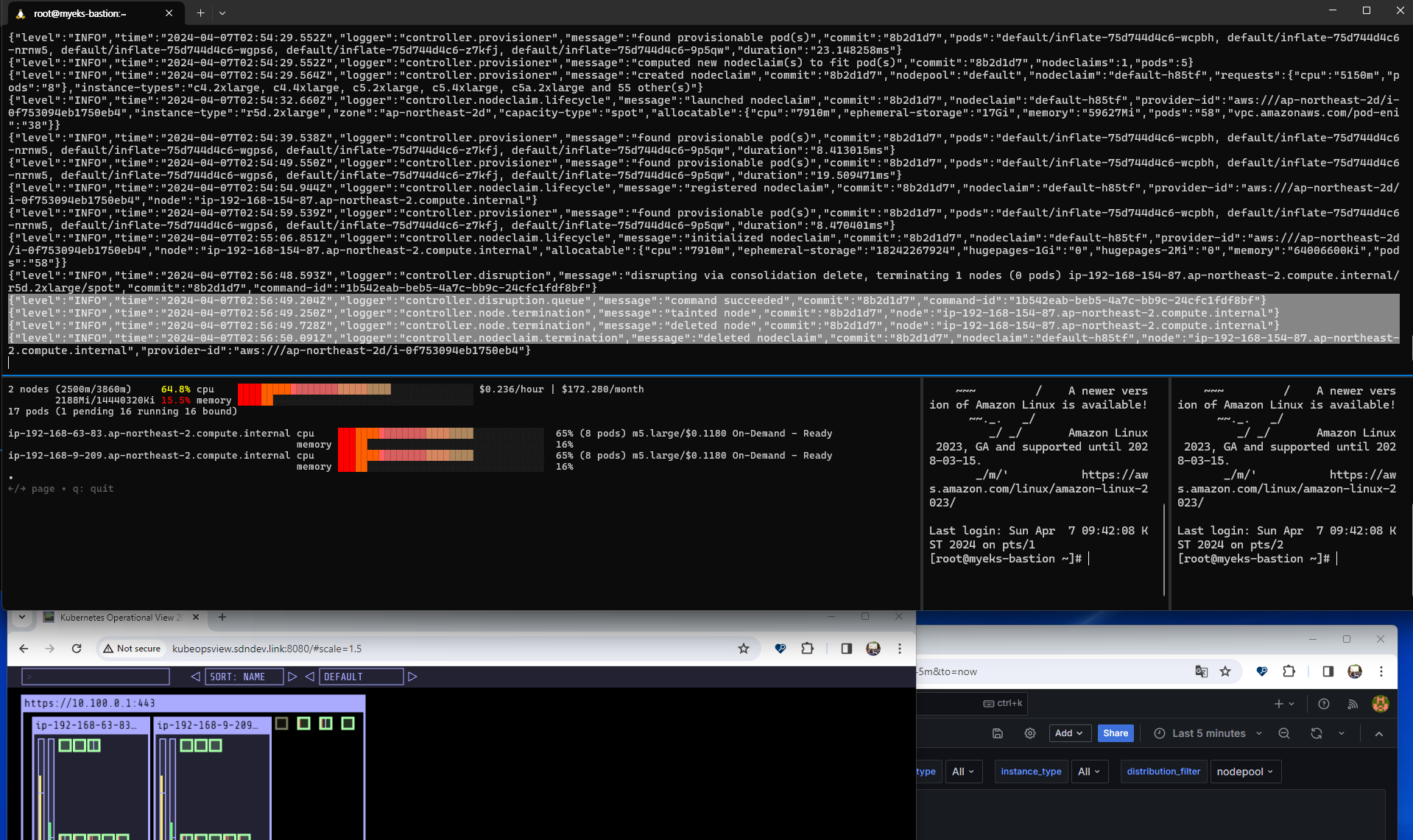
노드 개수가 다시 2개로 줄어든 것을 확인할 수 있었다.

그 다음에는 Disruption (구 Consolidation)을 테스트해보자. 중단 가능한 노드를 발견하고 필요할 대 교체를 시작하는 것으로, NodePool 또는 EC2NodeClass를 통해 구성 변경 사항을 자동으로 감지하여 필요한 변경 사항을 적용한다. 따라서 EKS를 보다 비용 효율적인 방식으로 사용할 수 있다는 장점을 가져다준다.

다음 예제를 통해 replica를 5개로 두었던 파드에 대해 1개로 변경하면서 최적 노드를 새로 만드는 실습을 수행한다.
# 기존 nodepool 삭제
kubectl delete nodepool,ec2nodeclass default
# v0.34.0 부터 featureGates 에 spotToSpotConsolidation 활성화로 사용 가능
helm upgrade karpenter -n kube-system oci://public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter --reuse-values --set settings.featureGates.spotToSpotConsolidation=true
# Create a Karpenter NodePool and EC2NodeClass
cat <<EOF > nodepool.yaml
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1beta1
kind: NodePool
metadata:
name: default
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
intent: apps
spec:
nodeClassRef:
name: default
requirements:
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["spot"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-category
operator: In
values: ["c","m","r"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-size
operator: NotIn
values: ["nano","micro","small","medium"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-hypervisor
operator: In
values: ["nitro"]
limits:
cpu: 100
memory: 100Gi
disruption:
consolidationPolicy: WhenUnderutilized
---
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1beta1
kind: EC2NodeClass
metadata:
name: default
spec:
amiFamily: Bottlerocket
subnetSelectorTerms:
- tags:
karpenter.sh/discovery: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" # replace with your cluster name
securityGroupSelectorTerms:
- tags:
karpenter.sh/discovery: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" # replace with your cluster name
role: "KarpenterNodeRole-${CLUSTER_NAME}" # replace with your cluster name
tags:
Name: karpenter.sh/nodepool/default
IntentLabel: "apps"
EOF
kubectl apply -f nodepool.yaml
# Deploy a sample workload
cat <<EOF > inflate.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: inflate
spec:
replicas: 5
selector:
matchLabels:
app: inflate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: inflate
spec:
nodeSelector:
intent: apps
containers:
- name: inflate
image: public.ecr.aws/eks-distro/kubernetes/pause:3.2
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 1.5Gi
EOF
kubectl apply -f inflate.yaml
#
watch -d "kubectl get nodes -L karpenter.sh/nodepool -L node.kubernetes.io/instance-type -L topology.kubernetes.io/zone -L karpenter.sh/capacity-type"
kubectl get nodes -L karpenter.sh/nodepool -L node.kubernetes.io/instance-type -L topology.kubernetes.io/zone -L karpenter.sh/capacity-type
# Scale in a sample workload to observe consolidation
# To invoke a Karpenter consolidation event scale, inflate the deployment to 1. Run the following command:
kubectl scale --replicas=1 deployment/inflate
kubectl -n kube-system logs -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter --all-containers=true -f --tail=20
kubectl get nodes -L karpenter.sh/nodepool -L node.kubernetes.io/instance-type -L topology.kubernetes.io/zone -L karpenter.sh/capacity-type
kubectl get node --label-columns=eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType,karpenter.sh/capacity-type
kubectl get node --label-columns=node.kubernetes.io/instance-type,topology.kubernetes.io/zone
# Use kubectl get nodeclaims to list all objects of type NodeClaim and then describe the NodeClaim Kubernetes resource
# using kubectl get nodeclaim/<claim-name> -o yaml.
# In the NodeClaim .spec.requirements, you can also see the 15 instance types passed to the Amazon EC2 Fleet API:
kubectl get nodeclaims
NAME TYPE ZONE NODE READY AGE
default-w52c4 c6g.large ap-northeast-2d ip-192-168-77-172.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal True 3m8s
kubectl get nodeclaims -o yaml | kubectl neat | yh
....
spec:
nodeClassRef:
name: default
requirements:
- key: karpenter.sh/nodepool
operator: In
values:
- default
- key: node.kubernetes.io/instance-type
operator: In
values:
- c6g.large
- c6gd.large
- c6gn.large
- c6id.large
- c6in.large
- c7g.large
- c7i.large
- m6g.large
- m6gd.large
- m6i.large
- m7g.large
- m7i-flex.large
- m7i.large
- r6g.large
- r7g.large
# 삭제
kubectl delete deployment inflate
kubectl delete nodepool,ec2nodeclass default
잘 실행되었고 아래와 같이 스크린샷을 찍어보았다.


살펴보면 이전 c6gd.large에서 m6g.large로 변경된 것을 확인할 수 있다. 메모리가 2배로 되어 있어 replica를 1개로 합치면 1.5g x 5 = 7.5g가 되고 따라서 메모리 8기가까지 수용 가능한 m6g.large 노드에 최적화시켜 할당한 것으로 분석된다.


실습을 완료한 이후에는 리소스를 삭제하고 종료하도록 하자.
# Karpenter IAM Role 생성한 CloudFormation 삭제
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name "Karpenter-${CLUSTER_NAME}"
# EC2 Launch Template 삭제
aws ec2 describe-launch-templates --filters "Name=tag:karpenter.k8s.aws/cluster,Values=${CLUSTER_NAME}" |
jq -r ".LaunchTemplates[].LaunchTemplateName" |
xargs -I{} aws ec2 delete-launch-template --launch-template-name {}
# 클러스터 삭제
eksctl delete cluster --name "${CLUSTER_NAME}"
# 위 삭제 완료 후 아래 삭제
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name myeks2
'Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AEWS] 스터디 7주차 - EKS CI/CD (0) | 2024.04.15 |
|---|---|
| [AEWS] 스터디 6주차 - EKS Security (0) | 2024.04.14 |
| [AEWS] 스터디 4주차 - Observability (0) | 2024.03.31 |
| [AEWS] 스터디 3주차 - EKS Storage & Nodegroup (0) | 2024.03.24 |
| [AEWS] 스터디 2주차 - EKS Networking (0) | 2024.03.17 |